In the past few weeks there have been a series of phishing attacks aimed at a small subset of Runbox customers. The goal of these scams is to trick unsuspecting email users into clicking on malicious web links and entering their Runbox username and password, enabling the scammers to steal their password.
At Runbox we are constantly on guard against phishing attacks against our customers, and here we take a closer look at this increasing problem and some simple steps you can take to protect yourself.
As a summary, ensure that you check:
- The From address. Phishing messages almost always come from a random email address that do not match our list of Official Runbox Email Addresses.
- The message addresses you by name. Scammers typically only have lists of email addresses without any first or last names, so if the message does not address you by your first and last name it is likely to be a scam.
- The legitimacy of any email with links. Check where the link will actually take you. Hover over it with your mouse, and you can see whether it will in fact take you to some random address not associated with Runbox at all.
- Any false urgency. Runbox will never pressure you to act suddenly. Scammers may try to create a sense of urgency to persuade you to do what they’re asking.
What is phishing?
Phishing is a type of cyber attack in which an attacker attempts to obtain sensitive information such as usernames, passwords, or credit card details by posing as a trustworthy entity via email messages.
The word “phishing” is derived from fishing and refers to using lures to “fish” for sensitive information. Phishing attacks typically use social engineering to gain a victim’s trust, and use spoofing such as faking an email address or URL to make the attack appear legitimate.
When phishing attacks are targeted at certain services or individuals it’s called “spear phishing”, and in this case they appear to be sent from Runbox Support, the Runbox Team, or other similar official sounding names.
Email users who are unfortunate enough to receive a spear phishing message and end up divulging their Runbox login details can end up having their Runbox accounts hijacked and used to send spam, which then forces us to suspend the accounts until the customer can regain access.
With access to an email user’s account the attackers may then be able to access their personal information and use it to commit fraud or identity theft, which can in turn result in financial loss or worse.
Naturally such account hijacking causes much confusion for the affected customers in addition to the privacy intrusion and consequences for the recipients of the spam being sent, which is often another phishing scam. The phishing then continues to cascade to new groups of innocent users of other email services, while exploiting people’s trust and rarely being caught.
It is important to understand that these scammers are criminals, and that being tricked into disclosing any login details can have serious consequences.
How to spot phishing
The easiest way to see whether a message is in fact from Runbox is to check the From address, as phishing emails almost always come from a random email address not on any Runbox domain names such as runbox.com.
You can find more details on this here: How can I tell whether an email is legitimate?
Another important clue is whether the email addresses you by name, or whichever name you have entered in your Runbox Account details. Attackers typically only have lists of email addresses without any first or last names, so if the message does not address you by name it is likely to be a scam.
The third way to check the legitimacy of any email which asks you to click on a link, is to check where the link will actually take you. Some phishing links look like they link to a Runbox web page, but if you hover over it with your mouse, you can see that it will in fact take you to some random address not associated with Runbox at all.
If in doubt, go to our main website Runbox at https://runbox.com for information, or contact us via Runbox Support at https://support.runbox.com.
Do not be fooled or threatened by the scams
Most phishing emails have a very urgent and even threatening tone, trying to scare the recipient into acting right away to avoid having their account shut down or disrupted.
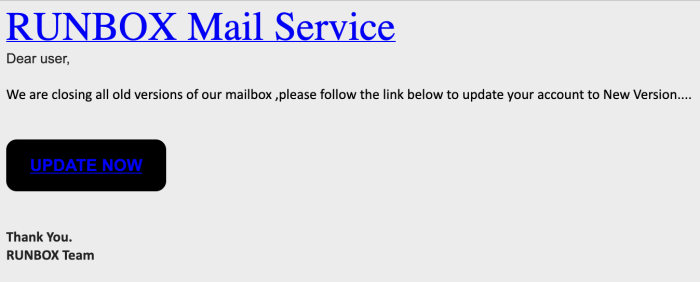
The scammers might even read our blog or other web pages and notice that we have two webmail versions, and subsequently send messages claiming that if you don’t switch to the newer version within X days, then your account will be shut down, for instance.
Legitimate messages from the Runbox Team will always give notice about something happening in the future, or optional new features.
Catching the scammers
We are constantly working to improve our defenses against phishing attacks, spam, and viruses, and we take immediate action to remove spear phishing messages as soon as we become aware of an attack.
If you have received any scam emails like the ones described above without responding in any way then your account is perfectly safe. We do however appreciate you notifying us via Runbox Support at https://support.runbox.com so that we can take steps to protect you and our other customers against the attack.
We also highly recommend enabling our Two-Factor Authentication features, which will keep your account safe even if your password should be stolen. For more on this, please see our Account Security Help page at https://help.runbox.com/account-security/.
If you have any doubts about an email you have received, then please don’t hesitate to contact Runbox Support at https://support.runbox.com.
